How to Tax Save Income for Salaried and Professionals for FY 2021-22? – a question that is often asked by my friends, family and blog readers. This is expected mainly due to the complicated income tax structure. There are multiple tax sections and every year a few more are added or modified. It’s hard to keep track of all of these and check if it’s applicable to you. To help both salaried and professionals in their tax planning, we have come up with the eBook “How to Tax Save for FY 2021-22”. This is a concise 43 slide power point presentation (in pdf) which covers all the income tax saving sections and investments applicable for tax payers.
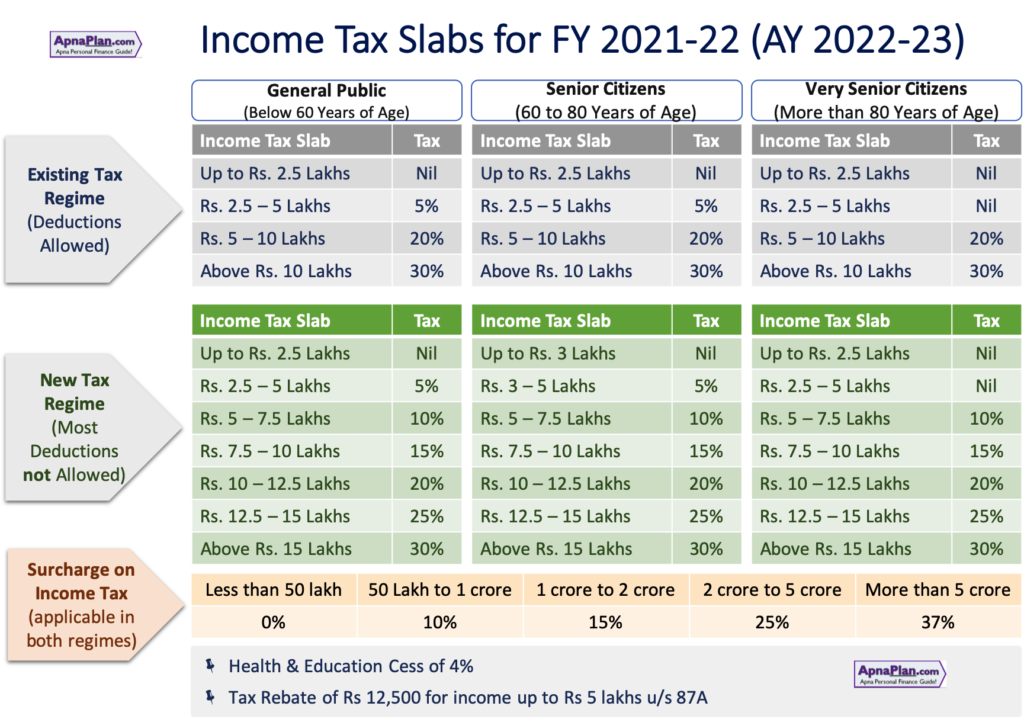
Lets have a look at the changes that happened in Income Tax laws in Budget 2021.
Budget 2021: Changes in Income Tax Rules
Thankfully in Budget 2021, there were very minor changes to the Income Tax Laws. There was no change in the income tax slab and you still have the option to choose between the Old & New Tax regime.
- No Change in Tax Slabs: The tax slabs remain unchanged from last year
- The choice between Old & New Tax regime remains
- Interest earned on contribution of more than Rs 2.5 Lakhs every year in EPF/VPF would be added to the income and taxed accordingly
- ULIPs would be taxed at 10% on maturity if premium exceeds Rs 2.5 lakhs in a year (similar to Equity Mutual Funds)
How to Pay 0 Income Tax on Salary of Rs 20+ Lakh?
Salary components and salary structure plays a very important role in how much income tax you pay. We have come up with some optimised salary structure using which you pay NO income tax even with CTC of more than Rs 20 Lakhs.
Mentioning Points I am frequently asked
- There is NO tax benefit on Infrastructure Bonds
- There is NO separate tax slab for Men & Women
I think on some platforms the above button is not clear, in that case CLICK Here to Download the Tax Planning ebook (How to Tax Save)
We give a brief of all the tax saving sections below:
How much Taxes you Need to Pay this Year? Download Our Income Tax Calculator to Know your Numbers
Do you know how much tax you need to pay for the year? Have you taken benefit of all tax saving rules and investments? How to Tax Save? Should you use the “NEW” tax regime or continue with the old one? In case you have all these questions just Download the Free Excel Income Tax Calculator for FY 2021-22 (AY 2022-23) and get your answers.
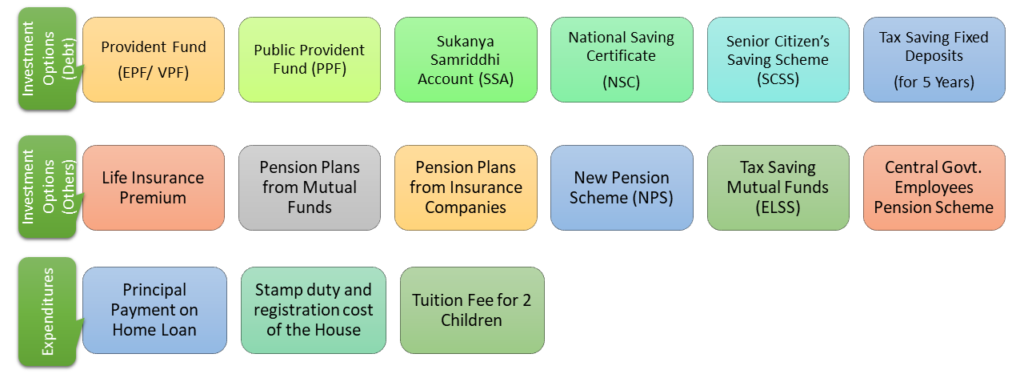
Section 80C/80CCC/80CCD (Save Tax by Investing)
How to Tax Save? These 3 are the most popular sections for tax saving and have lot of options to save tax. The maximum exemption combining all the above sections is Rs 1.5 lakhs. 80CCC deals with the pension products while 80CCD includes Central Government Employee Pension Scheme.
You can choose from the following for tax saving investments:
- Employee/ Voluntary Provident Fund (EPF/VPF)
- PPF (Public Provident fund)
- Sukanya Samriddhi Account
- National Saving Certificate (NSC)
- Senior Citizen’s Saving Scheme (SCSS)
- 5 years Tax Saving Fixed Deposit in banks/post offices
- Life Insurance Premium
- Pension Plans from Life Insurance or Mutual Funds
- NPS
- Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS – popularly known as Tax Saving Mutual Funds)
- Central Government Employee Pension Scheme
- Principal Payment on Home Loan
- Stamp Duty and registration of the House
- Tuition Fee for 2 children
Best Investment to Save Tax
Section 80C offers more than 10 investments where you can invest to save tax, However many a times you need not actually do this investment as its already covered due to expenses like children tuition fee or automatic EPF deduction for salaried. In case you are new to taxes and investment do read our helpful guide on How to take maximum advantage of Section 80C and choose the best investment to save tax.
Section 80CCD(1B) – Save Tax by Investing in NPS
Budget 2015 has allowed additional exemption of Rs 50,000 for investment in NPS. This is continued this year too. We have done a complete analysis which you can read by clicking the link here.
Payment of interest on Home Loan (Section 24)
The interest paid up to Rs 2 lakhs on home loan for self-occupied or rented home is exempted u/s 24. Earlier there was NO limit on interest deduction on rented property. Budget 2017 has changed this and now the tax exemption limit for interest paid on home loan is Rs 2 lakhs, irrespective of it being self-occupied or rented. However for rented homes any loss in excess of Rs 2 lakhs can be carried forward for up to 7 years.
HRA & Home Loan Benefit at same Time – Possible?
Many employer (& employers) are confused if they can take advantage of both HRA and Home Loan for saving tax. This seems intuitive as how can you pay for home loan and also live on rent. However just for your information its completely legal to take advantage of both HRA & Home Loan as there are multiple situations where you need to live on rent but still pay home loan. You can read more about this our post – Can I claim Tax Benefit on both HRA & Home Loan?
Payment of Interest on Education Loan (Section 80E)
How to Tax Save on Loan repayment? The entire interest paid (without any upper limit) on education loan in a financial year is eligible for deduction u/s 80E. However there is no deduction on principal paid for the Education Loan.
The loan should be for education of self, spouse or children only and should be taken for pursuing full time courses only. The loan has to be taken necessarily from approved charitable trust or a financial institution only.
The deduction is applicable for the year you start paying your interest and seven more years immediately after the initial year. So in all you can claim education loan deduction for maximum eight years.
Medical insurance for Self and Parents (Section 80D)
Premium paid for Mediclaim/ Health Insurance for Self, Spouse, Children and Parents qualify for deduction u/s 80D. You can claim maximum deduction of Rs 25,000 in case you are below 60 years of age and Rs 50,000 above 60 years of age.
An additional deduction of Rs 25,000 can be claimed for buying health insurance for your parents (Rs 50,000 in case of either parents being senior citizens). This deduction can be claimed irrespective of parents being dependent on you or not. However this benefit is not available for buying health insurance for in-laws.
HUFs can also claim this deduction for premium paid for insuring the health of any member of the HUF.
To avail deduction the premium should be paid in any mode other than cash. Budget 2013 had introduced deduction of Rs 5,000 (with in the Rs 25,000/30,000 limit) is also allowed for preventive health checkup for Self, Spouse, dependent Children and Parents. Its continued to this year too.
23 Most common Investments and How they are Taxed in 2021?
Taxes eat a large chunk of returns that we make on investments. Keeping this in mind we have compiled list taxes applicable for most common investments in India. We cover everything from fixed deposit to stock markets to real estate.

Treatment of Serious disease (Section 80DDB)
Cost incurred for treatment of certain disease for self and dependents gets deduction for Income tax. For senior citizens the deduction amount is up to Rs 1,00,000; while for all others its Rs 40,000. Dependent can be parents, spouse, children or siblings. They should be wholly dependent on you.
To claim the tax exemption you need a certificate from specialist from Government Hospital as proof for the ailment and the treatment. In case the expenses have been reimbursed by the insurance companies or your employer, this deduction cannot be claimed.In case of partial reimbursement, the balance amount can be claimed as deduction
Diseases Covered:
- Neurological Diseases
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Malignant Cancers
- AIDS
- Chronic Renal failure
- Hemophilia
- Thalassaemia
Physically Disabled Tax payer (Section 80U)
Tax Payer can claim deduction u/s 80U in case he suffers from certain disabilities or diseases. The deduction is Rs 75,000 in case of normal disability (40% or more disability) and Rs 1.25 Lakh for severe disability (80% or more disability)
A certificate from neurologist or Civil Surgeon or Chief Medical Officer of Government Hospital would be required as proof for the ailment.
Disabilities Covered
- Blindness and Vision problems
- Leprosy-cured
- Hearing impairment
- Locomotor disability
- Mental retardation or illness
- Autism
- Cerebral Palsy
Should you Invest in Gold?
We looked at more than 55 years history of gold to see if its a good idea to invest in Gold. We concluded that its more volatile than perceived but investing in long term may provide you with more stable returns. You can look at the complete analysis and our conclusion here – Looking at Gold Price History in India – Should you Invest in Gold?
Physically Disabled Dependent (Section 80DD)
In case you have dependent who is differently abled, you can claim deduction for expenses on his maintenance and medical treatment up to Rs 75,000 or actual expenditure incurred, whichever is lesser. The limit is Rs 1.25 Lakh for severe disability conditions i.e. 80% or more of the disabilities. Dependent can be parents, spouse, children or siblings. Also the dependent should not have claimed any deduction for self disability u/s 80DDB.
To claim the tax benefit you would need disability certificate issued by state or central government medical board.
You can also claim tax exemption on premiums paid for life insurance policy (in tax payers’ name) where the disabled person is the beneficiary. In case the disabled dependent expires before the tax payer, the policy amount is returned back and treated as income for the year and is fully taxable.
40% or more of following Disability is considered for purpose of tax exemption
- Blindness and Vision problems
- Leprosy-cured
- Hearing impairment
- Locomotor disability
- Mental retardation or illness
- Autism
- Cerebral Palsy
Donations to Charitable Institutions (Section 80G)
How to Tax Save by donations? The government encourages us to donate to Charitable Organizations by providing tax deduction for the same u/s 80G. Some donations are exempted for 100% of the amount donated while for others its 50% of the donated amount. Also for most donations, the maximum exemption you can claim is limited to 10% of your gross annual income. Please note that only donations made in cash or cheque are eligible for deduction. Donations in kind like giving clothes, food, etc is not covered for tax exemption.
How to Claim Sec 80G Deduction?
- A signed & stamped receipt issued by the Charitable Institution for your donation is must
- The receipt should have the registration number issued by Income Tax Dept printed on it
- Your name on the receipt should match with that on PAN Number
- Also the amount donated should be mentioned both in number and words
Donations for Scientific Research (Section 80GGA)
100% tax deduction is allowed for donation to the following for scientific research u/s 80GGC
- To a scientific research association or University, college or other institution for undertaking of scientific research
- To a University, college or other institution to be used for research in social science or statistical research
- To an association or institution, undertaking of any programme of rural development
- To a public sector company or a local authority or to an association or institution approved by the National Committee, for carrying out any eligible project or scheme
- To the National Urban Poverty Eradication Fund set up
How Tax on Mutual Funds Impact your Returns?
Equity Mutual Funds are one of the best investments to generate wealth in the long run while Debt mutual funds are more suited to park money for the short term (as an alternative to fixed deposits). But as in case of any investment, the final returns are determined on the way these Mutual Funds are taxed. We discusses tax on mutual funds for FY 2021-22 [AY 2022-23] in all details.
Donations to Political Parties (Section 80GGC)
100% tax deduction is allowed for donation to a political party registered under section 29A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 u/s 80GGC.
How to Tax Save – House Rent in case HRA is not part of Salary (Section 80GG)
In case, you do not receive HRA (House Rent Allowance) as a salary component, you can still claim house rent deduction u/s 80GG. Tax Payer may be either salaried/pensioner or self-employed.
To avail this you need to satisfy the following conditions:
- The rent paid should be more than10% of the income
- No one in the family including spouse, minor children or self should own a house in the city you are living. If you own a house in different city, you have to consider rental income on the same
The House Rent deduction is lower of the 3 numbers:
- Rs. 5,000 per month [changed from Rs 2,000 to Rs 5,000 in Budget 2016]
- 25% of annual income
- (Rent Paid – 10% of Annual Income)
You need to fill form no 10BA along with the tax return form
Tax Free Salary Components
There are components in salary which are fully or partially tax exempt. For example HRA is tax exempt if you satisfy certain conditions. You can have the complete list in the post: Must have Tax Free components in Salary.
We hope that this eBook “How to Tax Save for FY 2021-22?” (in pdf format) would help you in understanding, planning and saving taxes.

It’s an interesting and useful article post for the income tax payer in India and NRIs. Thanks for sharing the tax planning ebook for FY 2021-22.